BRICS 2024: Unveiling the New Chairman and the Dynamic 5-Point Agenda
A significant development on the international stage - the new leadership and 5-point agenda of BRICS in 2024. Let's delve right into this fascinating subject and give you complete insights.
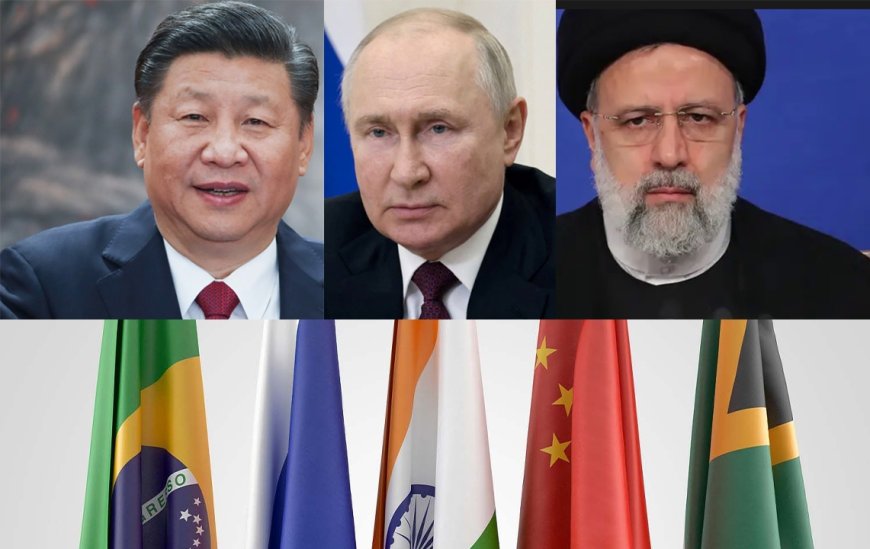

What is BRICS?
BRICS is an intergovernmental organization that comprises Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa. It has been commanding global attention since its inception. Originally identified to highlight investment opportunities, BRICS has transform into a formidable geopolitical force, coordinating multilateral policies since 2009 and hosting annual government summits.
The BRICS nations practice diplomatic relations primarily on a basis of non-interference, equality, and mutual benefit. The genesis of BRICS dates back to 2009 when the foundation members - Brazil, Russia, India, and China - held their initial summit in Yekaterinburg, with South Africa joining the bloc a year later. Evolution prevailed, and by January 2024, Egypt, Ethiopia, Iran, Saudi Arabia, and the United Arab Emirates were enveloped into the organization's fold.
Encapsulating approximately 30% of the world's land surface and home to 47% of the global population, the BRICS nations wield significant geopolitical heft. Brazil, Russia, India, and China are among the world's ten largest countries by population, area, and GDP (PPP). All initial five member states belong to the larger G20 assembly, with a combined nominal GDP of $28 trillion, representing about 27% of the gross world product. Their total GDP (PPP) is estimated at $57 trillion, accounting for a third of global GDP PPP, and their foreign reserves combine to an estimated $4.5 trillion (as of 2018).
Unsurprisingly, BRICS has emerged as the foremost geopolitical rival to the G7 bloc, comprised of the world's leading advanced economies. Rather than being merely reactive, BRICS has been proactive and innovative, implementing initiatives that directly compete with those of the G7 bloc. These initiatives include the New Development Bank, designed to mobilize resources for infrastructure and sustainable development projects; the BRICS Contingent Reserve Arrangement, established to provide short-term liquidity support; the BRICS payment system, aiming to reduce dependency on Western financial systems; the BRICS Joint Statistical Publication, dedicated to providing reliable and comparable statistical data; along with the BRICS basket of reserve currencies, designed to safeguard against global liquidity pressures.
BRICS 2024 New Chairman
The Russian president Vladimir Putin is now the new chairman of BRICS. At the beginning of this year, from the 1st of January 2024, five new countries joined BRICS, which include Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Ethiopia, Iran, and the United Arab Emirates. The Russian president has laid out his five principles or his five-point agenda, which includes consensus, sovereignty, mutual respect, the pursuit of a Multipolar world order, reducing redundancy on the Dollar, and creating an alternative system to the SWIFT system, the World Bank, and the IMF.
Putin's five-point agenda comprises consensus, sovereignty, mutual respect, the pursuit of a Multipolar world order, and reduction of redundancy on the Dollar. Each point symbolizes a different facet of Putin’s vision for the BRICS nations amidst global economic transformations.
Firstly, Putin's BRICS agenda calls for the idea of consensus; emphasizing a shared agreement on all economic, political, and trade issues within the group. Secondly, on the principle of sovereignty, Putin advocates for strengthened collective self-reliance among member countries. Thirdly, mutual respect, underpins the need for acknowledging each nation's unique political, economic, and social processes, thus promoting equality within the association.
Additionally, the call for a multipolar world order signifies Russia's aspiration to transform the global power structure by ending unilateral dominance and facilitating a more balanced, equitable platform for global decision-making. This principle emphasizes on Putin's stance against the domination of a singular power, particularly the United States.
Finally, Putin focuses on reducing dependence on the dollar and creating an alternative system to the SWIFT system, the World Bank, and the IMF.
The BRICS nations have pursued the idea of a separate financial mechanism for years, given their occasional disagreements with the traditional Western-led economic order. With Putin's proposition, the BRICS group might finally break free from existing financial structures. The initiative reflects Russia’s ambition to counter the Western financial dominance, alluding to the SWIFT system, dominated predominantly by the United States and several European countries. Russian leaders have long held concerns about their country's vulnerability due to its dependence on these systems.
BRICS expansion:
30 countries have applied for to join the BRICS Organization, below are some of the countries
Algeria applied in 2022 while Bahrain, Bangladesh, Belarus, Bolivia, Cuba , Kazakhstan, Kuwait, Pakistan, Palestine, Senega, Thailand, Venezuela, Vietnam and Nigeria applied in 2023.
BRICS Bank.
The New Development Bank (NDB), formerly known as the BRICS Development Bank, has taken center stage as an innovative multilateral development banking platform. This bank, primarily financed by Brazil, Russia, India, China, and South Africa, has come to represent an institution that stands as an instrument of growth and sustainability.
The main operational remit of the NDB lies in leveraging the strong economic capabilities of the BRICS countries, with the principal objective of funding infrastructure projects. Annually, it is authorized to lend up to $34 billion with each project targeting improvements to social and economic infrastructures depending on the individual needs of the borrowing country.
The BRICS Bank is located in South Africa, the African headquarters operates within the continent, offering easier and more direct access to funding for developing nations in Africa. This strategic location also demonstrates South Africa's commitment and the significance of their role within the BRICS financial milieu.
In terms of financials, the NDB started with an impressive capital base of $50 billion. This amount was equally contributed by the founding partners, each pledging $10 billion. However, with the forward-thinking strategy of the bank, it is projected that this wealth will increase to reach $100 billion over time.
In essence, the New Development Bank has emerged as a new pillar of global finance. The joint venture between BRICS states has not only solidified their own economies, but also facilitated other developing economies in need of funding for infrastructure projects. The bank’s continuous efforts towards inclusive growth, sustainability and its progressive approach fortifies its position on the global stage. This innovative multilateral growth and development-focused approach establishes the NDB as an important player in global financing.
BRICS payment system.
BRICS is developing new payment system to rival the globally predominant SWIFT system. The SWIFT (Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication).
The primary intention of this strategic move was to transition towards settlements in national currencies, a shift away from the dollar-centric global financial mechanism. This step has the potential of enhancing economic stability by insulating these countries from volatile currency fluctuations and policy decisions of externally-dominant economies.
The Central Bank of Russia affirmed the importance of this alternative system by underscoring its role as a backup and redundancy measure, safeguarding against possible future disruptions to the SWIFT system. It was an evident step towards achieving financial autonomy and security, reflecting prudence in proactively managing strategic financial risks that may arise in a globally inter-linked and complex economic reality.
Meanwhile, China launched its own replacement for SWIFT, the Cross-Border Interbank Payment System (CIPS). This system, like SWIFT, enables fiscal institutions across the globe to send and receive data regarding financial transactions. CIPS reflects China's ongoing economic growth and its prominent role in global financial dynamics.
Russia also launched its own national payment messaging system, known as the SPFS (System for Transfer of Financial Messages), while Brazil introduced Pix, a system focused on instant payment methodology.
These SWIFT-alternatives represent an increasing demand for economic self-reliance and resilience, while equally offering potential challenges to the dollar-centric global financial regime.